About Me
Upon returning to India, I advanced my expertise at the Robotics Research Center at IIIT Hyderabad, where I built SLAM-based robotic systems using ROS. This was followed by a role where I designed and launched IoT-driven products, including an Inventory Management System, a CNC Laser Engraving Machine, and an Autonomous Workshop Cleaning Robot. Concurrently, I gained experience with machine vision-based diagnostics and contributed to an AI-driven personalized learning platform.
Today, I serve as the Chief Technology Officer at Cloud Ladder Consulting, leading a 15-member team in the delivery of AI/ML-powered, cloud-native solutions across healthcare, logistics, and finance, improving client efficiency by up to 30%. My focus includes implementing MLOps pipelines, which has reduced model deployment time from weeks to days.
Alongside my work, I serve as a Subject Matter Expert (AI/ML, IoT, Robotics) with Gujarat Council on Science and Technology (GUJCOST), Department of Science & Technology, Government of Gujarat, and as the National President of the National Science & Technology Forum Mission New India, Narendra Modi Vichar Manch (NMVM).
My passion lies in advancing research and innovation in AI, IoT, and Robotics. I am dedicated to bridging the gap between deep tech and business strategy to build scalable, human-centered solutions that deliver demonstrable ROI and drive both commercial success and positive social impact.
Domains

Healthcare
Application of AI in healthcare can help address issues of high barriers to access to healthcare facilities, particularly in rural areas that suffer from poor connectivity and limited supply of healthcare professionals. This can be achieved through implementation of use cases such as AI driven diagnostics, personalized treatment, early identification of potential pandemics, and imaging diagnostics, among others.

Agriculture
AI holds the promise of driving a food revolution and meeting the increased demand for food (global need to produce 50% more food and cater to an additional 2 billion people by 2050 as compared to today). It also has the potential to address challenges such as inadequate demand prediction, lack of assured irrigation, and overuse / misuse of pesticides and fertilizers. Some use cases include improvement in crop yield through real time advisory, advanced detection of pest attacks, and prediction of crop prices to inform sowing practices.
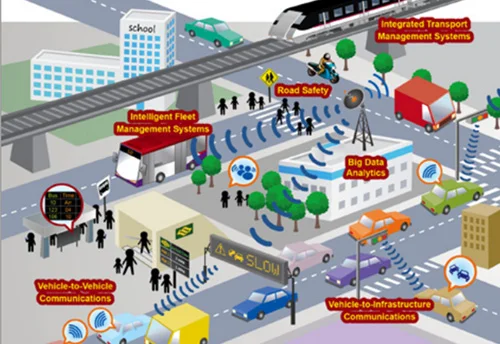
Smart Mobility, including Transports and Logistics
Potential use cases in this domain include autonomous fleets for ride sharing, semi-autonomous features such as driver assist, and predictive engine monitoring and maintenance. Other areas that AI can impact include autonomous trucking and delivery, and improved traffic management.

Retail
The retail sector has been one of the early adopters of AI solutions, with applications such as improving user experience by providing personalized suggestions, preference-based browsing and image-based product search. Other use cases include customer demand anticipation, improved inventory management, and efficient delivery management.

Manufacturing
Manufacturing industry is expected to be one of the biggest beneficiaries of AI based solutions, thus enabling 'Factory of the Future' through flexible and adaptable technical systems to automate processes and machinery to respond to unfamiliar or unexpected situations by making smart decisions. Impact areas include engineering (AI for R&D efforts), supply chain management (demand forecasting), production (AI can achieve cost reduction and increase efficiency), maintenance (predictive maintenance and increased asset utilization), quality assurance (e.g. vision systems with machine learning algorithms to identify defects and deviations in product features), and in-plant logistics and warehousing.

Energy
Potential use cases in the energy sector include energy system modeling and forecasting to decrease unpredictability and increase efficiency in power balancing and usage. In renewable energy systems, AI can enable storage of energy through intelligent grids enabled by smart meters, and also improve the reliability and affordability of photovoltaic energy. Similar to the manufacturing sector, AI may also be deployed for predictive maintenance of grid infrastructure.

Smart Cities
Integration of AI in newly developed smart cities and infrastructure could also help meet the demands of a rapidly urbanizing population and providing them with enhanced quality of life. Potential use cases include traffic control to reduce congestion and enhanced security through improved crowd management.

Education and Skilling
AI can potentially solve for quality and access issues observed in the Indian education sector. Potential use cases include augmenting and enhancing the learning experience through personalized learning, automating and expediting administrative tasks, and predicting the need for student intervention to reduce dropouts or recommend vocational training.

Vision 2050
» Advanced personalized learning
» Advanced health informatics
» Securing the cyberspace
» Defence
» Prevent nuclear and other forms of terror
» Develop carbon sequestration methods
» Restore and improve urban infrastructure
» Engineer better medicines,
» Provide access to clean water
» Food security and efficient agriculture
» Improving and encouraging the aquaculture
» Engineer the tools for scientific discovery
» Making solar energy affordable